The way organizations design and manage IT infrastructure has transformed drastically over the last two decades. From sprawling multi-site enterprise architectures to consolidated, high-performance virtualized data centers, and now into container-based platforms, the journey has been evolutionary.
This blog post explores the shift from traditional virtualized data centers to modern containerization technologies like OpenShift, focusing on how businesses can modernize their IT landscape to keep up with the demands of today’s dynamic applications.
Understanding the Evolution of IT Infrastructure
H3: The Multi-Site Enterprise Era
Before centralization, enterprises operated multi-site IT infrastructure setups across various cities or regions. For example, an organization might have had infrastructure hubs in Pune, Bangalore, Delhi, and Kolkata, each with its local servers, switches, and routers.
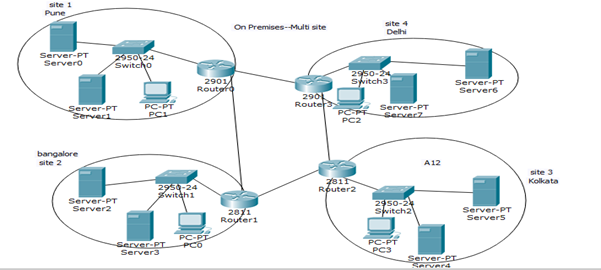
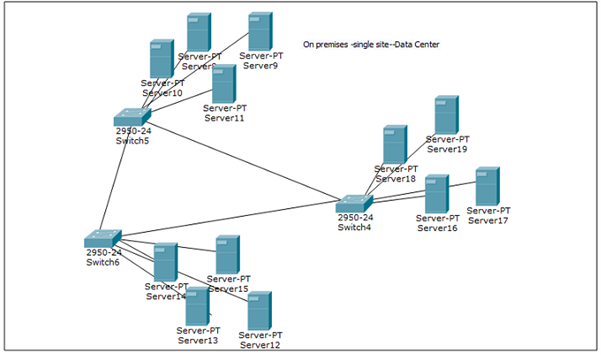
Rise of the Virtualized Data Center
With the emergence of virtualization technologies such as VMware ESXi and oVirt, organizations began consolidating these dispersed environments into centralized virtualized data centers.
Benefits of Virtualized Data Centers:
-
Efficient hardware utilization
-
Centralized management
-
Easier deployment and scaling
-
Platform independence
What is Virtualization in Enterprise IT?
Virtualization involves abstracting hardware resources and running multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server using a hypervisor.
Leading Virtualization Platforms
-
VMware ESXi: Industry leader with robust performance, widely adopted in enterprises.
-
oVirt: Open-source alternative, built for flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
These platforms allowed organizations to run applications like Active Directory, DNS, DHCP, storage, and web servers on virtual instances of Windows Server, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, and Unix systems.
Limitations of Virtualization in Modern Application Deployment
While revolutionary, virtual machines brought their own set of limitations:
-
Resource-intensive: Each VM requires its own OS.
-
Slow startup and scaling times.
-
Complexity in managing dependencies for microservices.
As DevOps, cloud-native architectures, and microservices gained popularity, the need for a more agile solution became clear.
The Shift to Containerization
Containerization emerged as the next step, addressing the shortcomings of virtualization by packaging applications and their dependencies into lightweight, portable units known as containers.
Containerization vs Virtualization
| Feature | Virtualization | Containerization |
|---|---|---|
| Isolation | OS-level | Process-level |
| Startup Time | Minutes | Seconds |
| Resource Usage | High | Low |
| Portability | Moderate | High |
| Ideal For | Monolithic apps | Microservices apps |
Introducing OpenShift: A Modern Container Platform
OpenShift is an enterprise-grade Kubernetes container platform developed by Red Hat. It is designed for:
-
Container orchestration
-
CI/CD pipelines
-
Hybrid cloud deployments
Key Features of OpenShift Container Platform
-
Built-in developer tools
-
Operator framework for automating operations
-
Self-healing and auto-scaling containers
-
Integration with GitOps and DevSecOps workflows
Containerization in DevOps & Cloud-Native Environments
Why DevOps Teams Prefer Containers
-
Rapid development and deployment
-
Simplified CI/CD integrations
-
Easy rollback and versioning
-
Environment consistency across dev, staging, and prod
DevOps + Containers = Modern Infrastructure
Container platforms like OpenShift enable seamless application delivery, especially for:
-
Microservices
-
Serverless computing
-
API-first applications
Real-World Example of Infrastructure Modernization
Consider an enterprise with a legacy, multi-site infrastructure:
-
4 geographically distributed sites (e.g., Pune, Bangalore, Delhi, Kolkata)
-
Each site had local servers, switches, and routers
They transitioned to a centralized virtualized data center, running applications on VMware ESXi.
Now, to meet modern scalability and agility requirements, they’ve migrated to OpenShift:
-
Deployed containerized apps with minimal overhead
-
Automated rollouts with Kubernetes
-
Integrated GitOps pipelines for deployment management
Benefits of Data Center Modernization with Containers
-
Faster Time to Market: Rapid app deployment and updates
-
Resource Efficiency: Containers are lightweight compared to VMs
-
Scalability: Auto-scale based on usage
-
Portability: Deploy across on-premise, hybrid, and public clouds
-
Enhanced Security: Isolation at the container level
Conclusion
The evolution from multi-site architectures to virtualized data centers, and now to containerized platforms like OpenShift, reflects how IT infrastructure is aligning with modern application demands. Enterprises that embrace this transformation gain not only agility and scalability but also a competitive edge in delivering digital services efficiently.
If you’re planning to modernize your IT environment, consider migrating from traditional virtualization to a robust, containerized ecosystem.
Comments are closed